BREAKING: Eighth Study Confirms mRNA Shots Increase Infection Risk
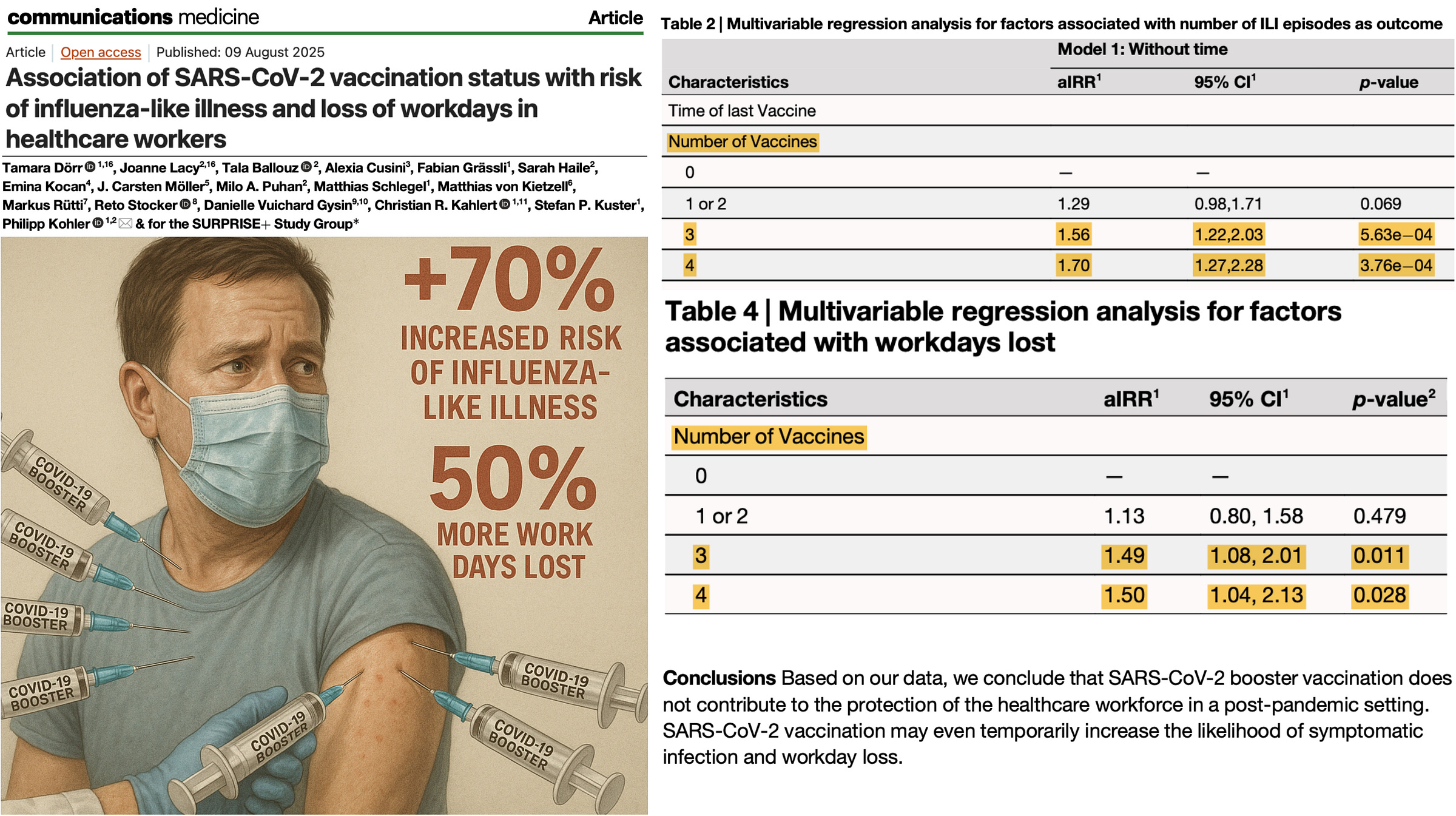
New study of 1,745 healthcare workers finds mRNA boosters raise risk of influenza-like illness by up to 70% and increase workdays lost by 50%.
A major Swiss study of 1,745 healthcare workers, published in Nature’s Communications Medicine, found that recent COVID-19 booster shots were linked to a significantly higher risk of illness and missed work compared to the unvaccinated.
The illness measured was Influenza-Like Illness (ILI) — sudden onset of fever (≥38°C or feeling feverish) plus at least one respiratory symptom (cough, sore throat, runny nose, loss of smell) within 7 days.
National surveillance showed that during the study period, ~21% of ILI cases were COVID-19, ~20% were influenza, and the rest were caused by other respiratory viruses — meaning boosters increase risk of infection from multiple different pathogens:
Higher Risk of Illness After Boosters
3 doses: aIRR 1.56 (95% CI 1.22–2.03) — 56% higher risk of ILI vs. unvaccinated.
4 doses: aIRR 1.70 (95% CI 1.27–2.28) — 70% higher risk.
More recent boosters: aIRR 1.32 (95% CI 1.07–1.62) — strongest effect soon after vaccination.
More Sick Days After Boosters
3 doses: aIRR 1.49 (95% CI 1.08–2.01) — 49% more workdays lost.
4 doses: aIRR 1.50 (95% CI 1.04–2.13) — 50% more workdays lost.
Robust Even After Adjusting for Confounders
Inverse probability weighting confirmed the association: recent boosters aIRR 1.26 (95% CI 1.12–1.43).
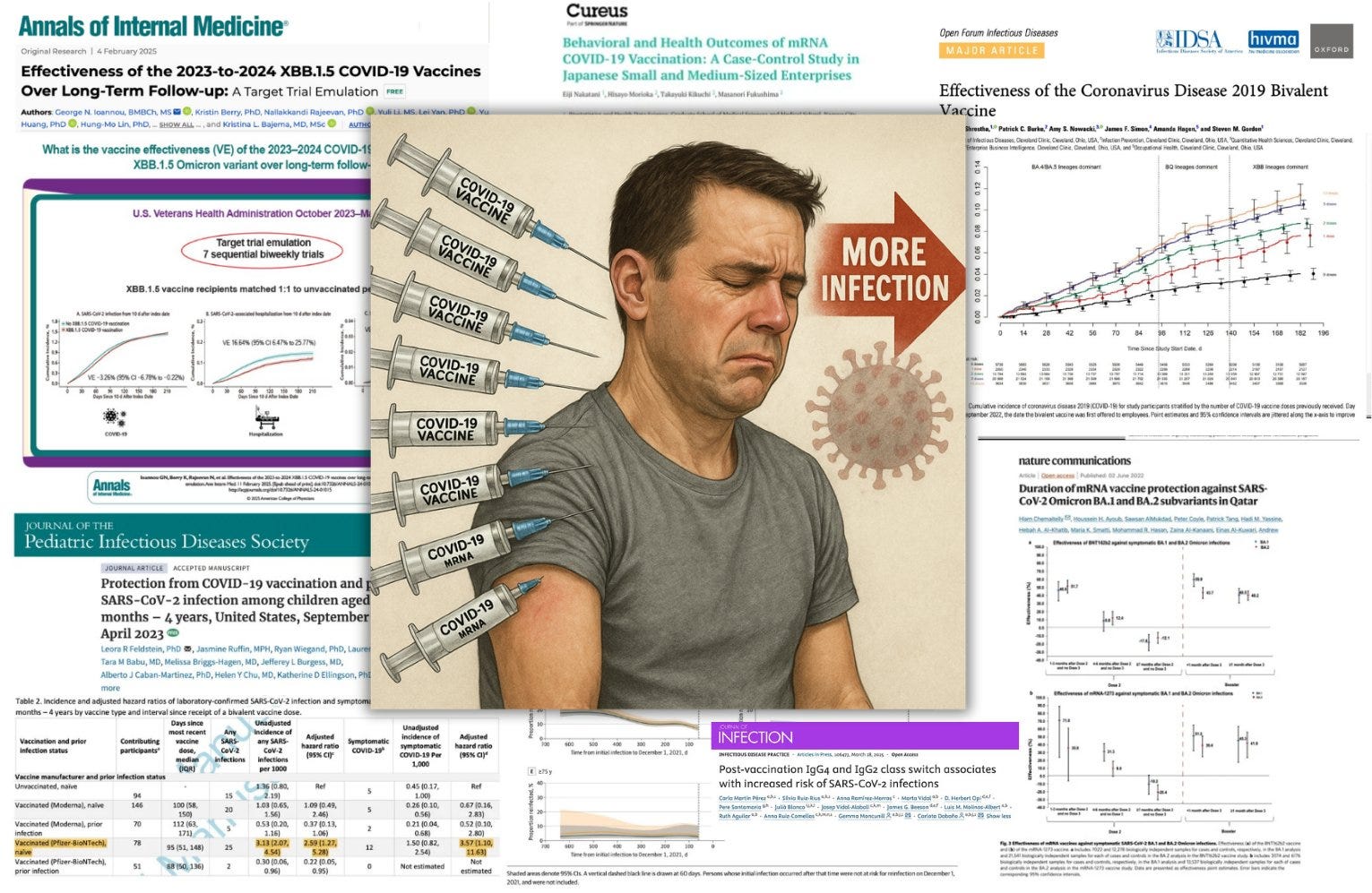
These Findings Corroborate SEVEN Other Studies Showing COVID-19 “Vaccines” Increase Infection Risk
Shrestha et al. (Cleveland Clinic) – COVID-19 risk increased with dose count:
1 dose → +107% risk (HR 2.07, 95% CI: 1.70–2.52)
≥3 doses → +253% risk (HR 3.53, 95% CI: 2.97–4.20)
Feldstein et al. (CDC) – Pfizer-vaccinated children without prior infection:
+159% risk of infection (HR 2.59, 95% CI: 1.27–5.28)
+257% risk of symptomatic COVID-19 (HR 3.57, 95% CI: 1.10–11.63)
Perez et al. – More mRNA doses → IgG4 antibody levels ↑ 11× → 1.8× higher infection risk.
Ioannou et al. – Vaccine effectiveness against infection was -3.26% (95% CI: -6.78% to -0.22%) — meaning higher infection rates in the vaccinated group.
Nakatani et al. – Vaccinated individuals had +85% infection odds vs. unvaccinated (OR 1.85, 95% CI: 1.33–2.57).
Eythorsson et al. – 2+ doses → +42% reinfection risk vs. ≤1 dose (95% CI: 1.13–1.78).
Chemaitelly et al. – Effectiveness against Omicron BA.1 & BA.2 infections turned negative within 7 months:
Pfizer: 46.6% → -17.8%, 51.7% → -12.1%
Moderna: 71.0% → -10.2%, 35.9% → -20.4%
These data make it clear: mRNA technology for infectious diseases is acting as an infection promoter. It’s time to return to common-sense public health principles and remove this dangerous gene-transfer platform from the market.
Epidemiologist and Foundation Administrator, McCullough Foundation
www.mcculloughfnd.org
Please consider following both the McCullough Foundation and my personal account on X (formerly Twitter) for further content.



Nicolas I just want to thank you again for your faithfulness in presenting the truth about this abominable mRNA “technology”, otherwise known as high tech poison.
And, not only do you present it faithfully and consistently but you also summarize and organize and demystify to the extent possible, the jargon and obfuscation which is inherent in scientific publications.
May the Lord bless you and your work for the Truth,
In Him,
Jacob
The flu shot made it more likely to catch covid - the covid shot makes it more likely to catch flu
Neither makes it less likely to catch either