STUDY: TikTok, Instagram, and YouTube Shorts Induce Measurable “Brain Rot”
Doomscrolling, zombie scrolling, and dopamine-driven streams of low-quality content are producing measurable cognitive impairment across an entire generation.
In 2024, “brain rot” went from an online meme to the Oxford Word of the Year.
‘Brain rot’ is defined as “the supposed deterioration of a person’s mental or intellectual state, especially viewed as the result of overconsumption of material (now particularly online content) considered to be trivial or unchallenging.”
Our experts noticed that ‘brain rot’ gained new prominence this year as a term used to capture concerns about the impact of consuming excessive amounts of low-quality online content, especially on social media. The term increased in usage frequency by 230% between 2023 and 2024.
The first recorded use of ‘brain rot’ was found in 1854 in Henry David Thoreau’s book Walden, which reports his experiences of living a simple lifestyle in the natural world. As part of his conclusions, Thoreau criticizes society’s tendency to devalue complex ideas, or those that can be interpreted in multiple ways, in favour of simple ones, and sees this as indicative of a general decline in mental and intellectual effort: “While England endeavours to cure the potato rot, will not any endeavour to cure the brain-rot – which prevails so much more widely and fatally?”
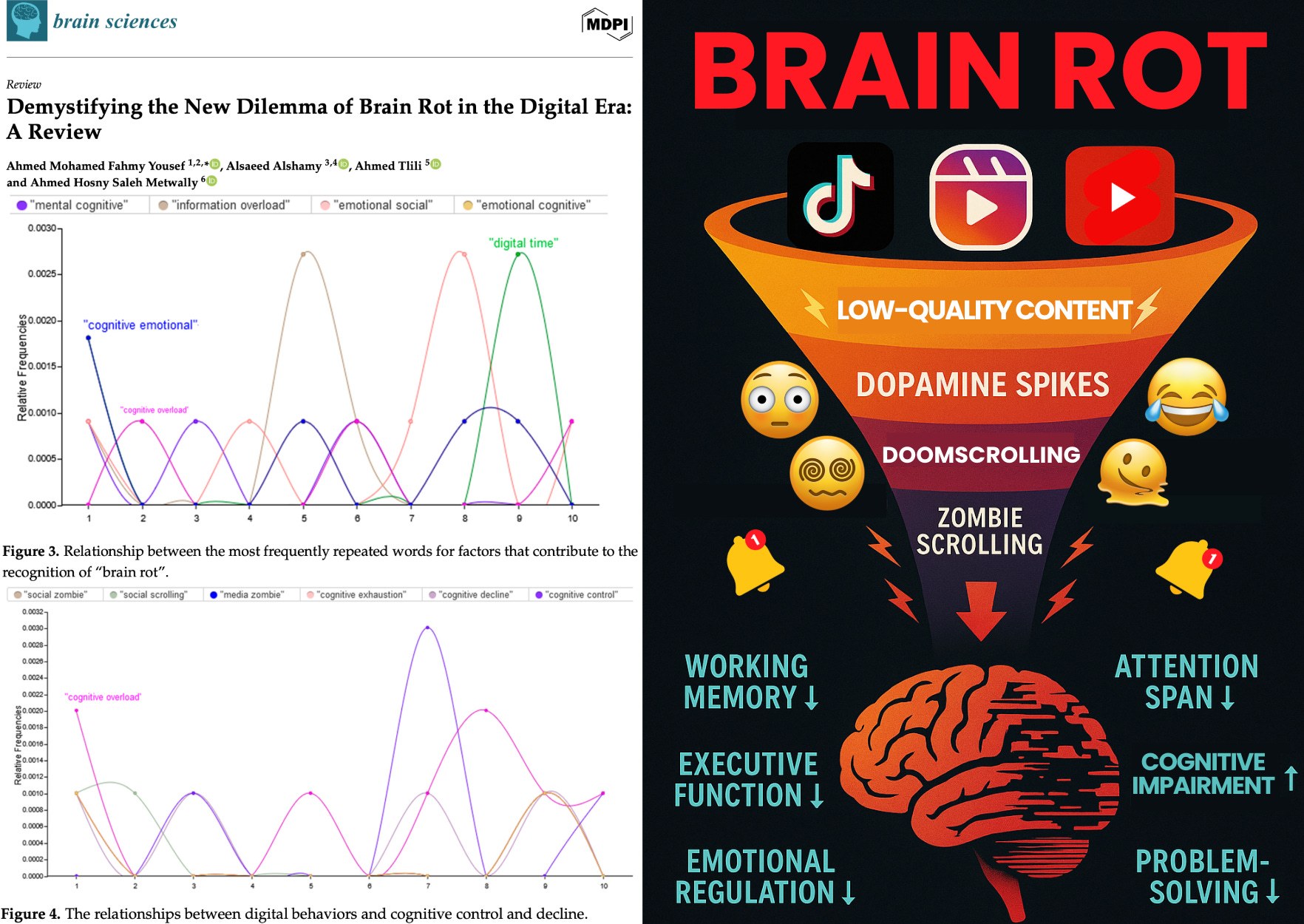
Now, a peer-reviewed paper titled, Demystifying the New Dilemma of Brain Rot in the Digital Era: A Review, confirms that brain rot is real: the digital environment is chemically, cognitively, and psychologically degrading the developing human brain. And the damage is measurable.
According to the study, brain rot isn’t a meme. It’s a documented state of cognitive atrophy, driven by overstimulation, dopamine feedback loops, and nonstop exposure to low-quality digital content.
The authors conducted a rapid review, systematically analyzing 381 studies, filtering to 35 high-quality papers published between 2023–2024. Here’s what they found:
The Core Mechanism: Overstimulation + Dopamine Feedback Loops
The review shows that young people now average 6.5 hours per day online — primarily on algorithm-driven platforms like TikTok, Instagram Reels, YouTube Shorts, and endless-scroll feeds engineered for split-second novelty.
Most of the content involves rapid, low-information stimuli: ultrashort videos, memes, reaction clips, and trivial entertainment fragments that provide novelty without cognitive substance.
These platforms deliver rapid bursts of artificially rewarding stimuli, creating a cycle of:
Constant cognitive overstimulation
The brain never enters a “rest” mode or deeper thought state.
Weakening of working memory
Information is consumed too quickly to be consolidated.
Fragmented attention networks
Short-form content trains the mind to expect constant novelty.
Difficulty processing long or complex information
Deep reading and sustained focus become neurologically harder.
Mental fatigue & reduced executive function
Chronic overstimulation taxes the prefrontal cortex — the center of planning, reasoning, and self-regulation.
The study describes this as a shift from healthy, top-down cognitive control to bottom-up, dopamine-seeking impulsivity.
Doomscrolling: Chronic Exposure to Negative, Threatening, or Grotesque Content
Many people casually use the term, but the study provides a precise functional definition:
Doomscrolling = the compulsive consumption of emotionally negative or threat-based content.
Doomscrolling produces:
Persistent anxiety and hypervigilance
The brain remains locked in a threat-detection mode.Rumination loops
Negative information gets replayed mentally.Physiological stress responses
Chronic cortisol elevation impairs cognition.Reduced memory formation
Stress disrupts hippocampal consolidation.Attentional fragmentation
The brain becomes primed for scanning, not focusing.
According to the review, doomscrolling directly impairs working memory, emotional regulation, and sustained attention, accelerating cognitive wear-and-tear.
Zombie Scrolling: The Dissociative “Mindless Drift” That Damages Cognition
Doomscrolling is emotionally intense. Zombie scrolling is emotionally empty.
Zombie scrolling = passive, intentionless, dissociative swiping through content with no goal, awareness, or engagement.
Zombie scrolling is associated with:
Dissociation
The mind drifts, reducing present-moment awareness.Working-memory depletion
Mindless consumption offers no cognitive stimulation.Reduced attentional control
The brain becomes conditioned to effortless, low-value input.Emotional numbing & detachment
Pleasure/reward pathways become desensitized.Diminished cognitive engagement
The brain stops initiating deeper thought patterns.
The review notes that zombie scrolling may be even more insidious because users don’t feel stressed, so they underestimate the damage — yet the cognitive decline accumulates quietly over time.
Preclinical Dementia Signatures Are Appearing in Younger Generations
A striking findings of the review is that digital-era cognitive decline now mirrors several early dementia–like neurobiological patterns. Across neuroimaging and behavioral studies, excessive digital exposure is linked to reduced hippocampal engagement, producing shallow, fragmented memory formation rather than durable consolidation.
At the same time, prefrontal cortex function—which governs planning, inhibition, and decision-making—shows measurable degradation under chronic multitasking and rapid-fire media input.
This constant overstimulation imposes a chronic cognitive load on the neocortex, creating patterns consistent with accelerated cognitive aging. Notably, several longitudinal findings suggest an elevated lifetime risk of cognitive decline, indicating these effects may not be transient. These changes are well-documented through fMRI and controlled studies included in the review, demonstrating that preclinical neurodegenerative signatures are already emerging in younger populations.
Brain Rot: A Real Neurocognitive Syndrome
The study shows a clear, repeatable pattern: excessive digital exposure to low-quality content degrades working memory, sustained attention, executive function, problem-solving, and emotional regulation. Constant notifications and rapid content switching impair information holding and focus, while overstimulation weakens planning, self-control, and cognitive flexibility.
Both doomscrolling’s emotional overload and zombie scrolling’s emotional emptiness destabilize the central nervous system, producing a more rigid, impulsive, and cognitively inefficient brain. Adolescents exhibit the most severe deficits, underscoring the risk of long-term impact.
The evidence confirms brain rot is real, emerging early, accelerating quickly, and consuming a generation.
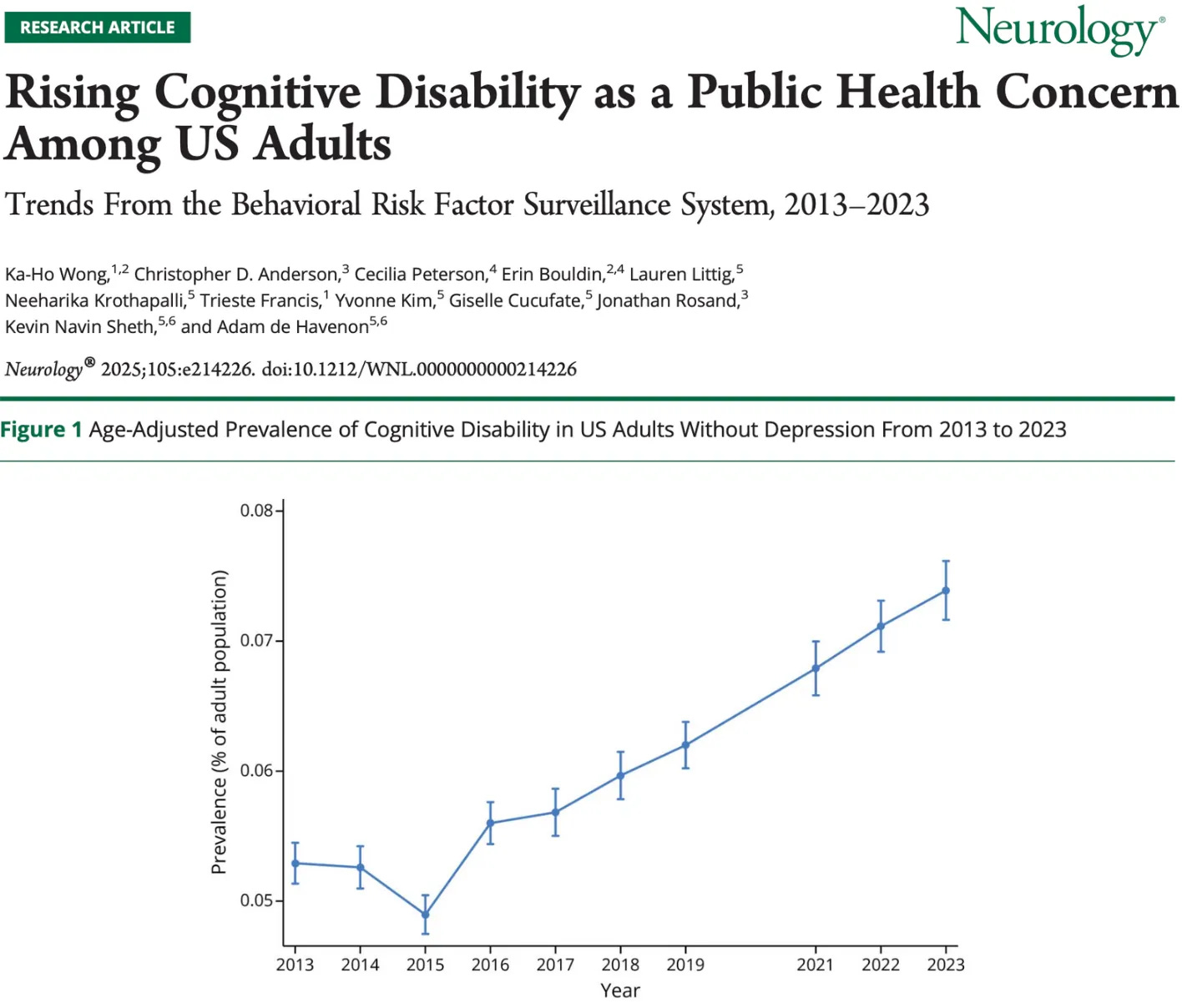
This is one of the core reasons why cognitive disability is now a public health concern in the United States. Cognitive impairment is skyrocketing with no end in sight:
Widespread cognitive decline before adulthood may soon become the norm as AI-generated “brain rot” content begins to drastically proliferate.
Epidemiologist and Foundation Administrator, McCullough Foundation
Support our mission: mcculloughfnd.org
Please consider following both the McCullough Foundation and my personal account on X (formerly Twitter) for further content.





Powerful & informative article - thank you. In 2022 Websters named 'gaslighting' as the word of the year. It's no surprise that it's migrated to 'brain rot' - this is not by accident but fully engineered by the corrupted/evil cabal. Grateful I spend more time with our Creator in prayer, in Nature & connecting with people in conversation than scrolling etc. In God we Trust ...
Iodine deficiency is rampant in addition. Look up findings re iodine and "brain fog." "Cretinism", the defined syndrome of congenital iodine deficiency, seems nowadays to solely be discussed in terms of thyroid function, but by 1900 it was well understood that the brain directly uses iodine--relies upon it--independent of thyroid function alone.